Forex fundamental analysis works by analysing economic data, central bank policy, and global risk conditions to determine relative currency strength before price moves. In practice, it translates macroeconomic reality into expectations about interest rates, capital flows, and risk appetite, which the foreign exchange market prices continuously.
Forex fundamental analysis is the process of using macroeconomic data and central bank policy to explain and anticipate currency price movement through relative strength between two economies.
How Forex Fundamental Analysis Works in One Sentence
Fundamentals move currencies because they change expectations for interest rates, growth, and capital flows, and the FX market prices those expectations continuously rather than waiting for the data itself.
Why Currencies Move Based on Fundamentals
Currencies are priced like a real-time referendum on an economy’s future. When investors expect higher real yields, stronger growth, or improving external balances, they demand that currency. Conversely, when they expect easing, slower growth, rising inflation without compensation, or deteriorating balances, they sell it.
Three core mechanisms link fundamentals to currency prices.
Interest rate expectations and yield differentials
Foreign exchange is heavily driven by where capital can earn the best risk-adjusted return. If one country is expected to keep rates higher for longer, or raise them sooner, its currency often strengthens. However, what matters most is the change in expectations, not the rate level already priced by the market.
Capital flows and portfolio allocation
Large global investors continuously reallocate capital across bonds, equities, and cash. Therefore, when a country’s assets become more attractive, inflows tend to support the currency. On the other hand, when investors hedge or exit, the currency often weakens.
Risk regimes and safe-haven behaviour
During risk-off regimes, capital typically seeks liquidity and safety. During risk-on regimes, it rotates into higher-yielding or growth-sensitive currencies. As a result, the same economic data can produce different FX outcomes depending on the broader global environment.
The Practical Step-by-Step Workflow
This workflow is designed to be repeatable and disciplined. Importantly, it prevents reactive headline trading and forces a clear separation between signal and noise.
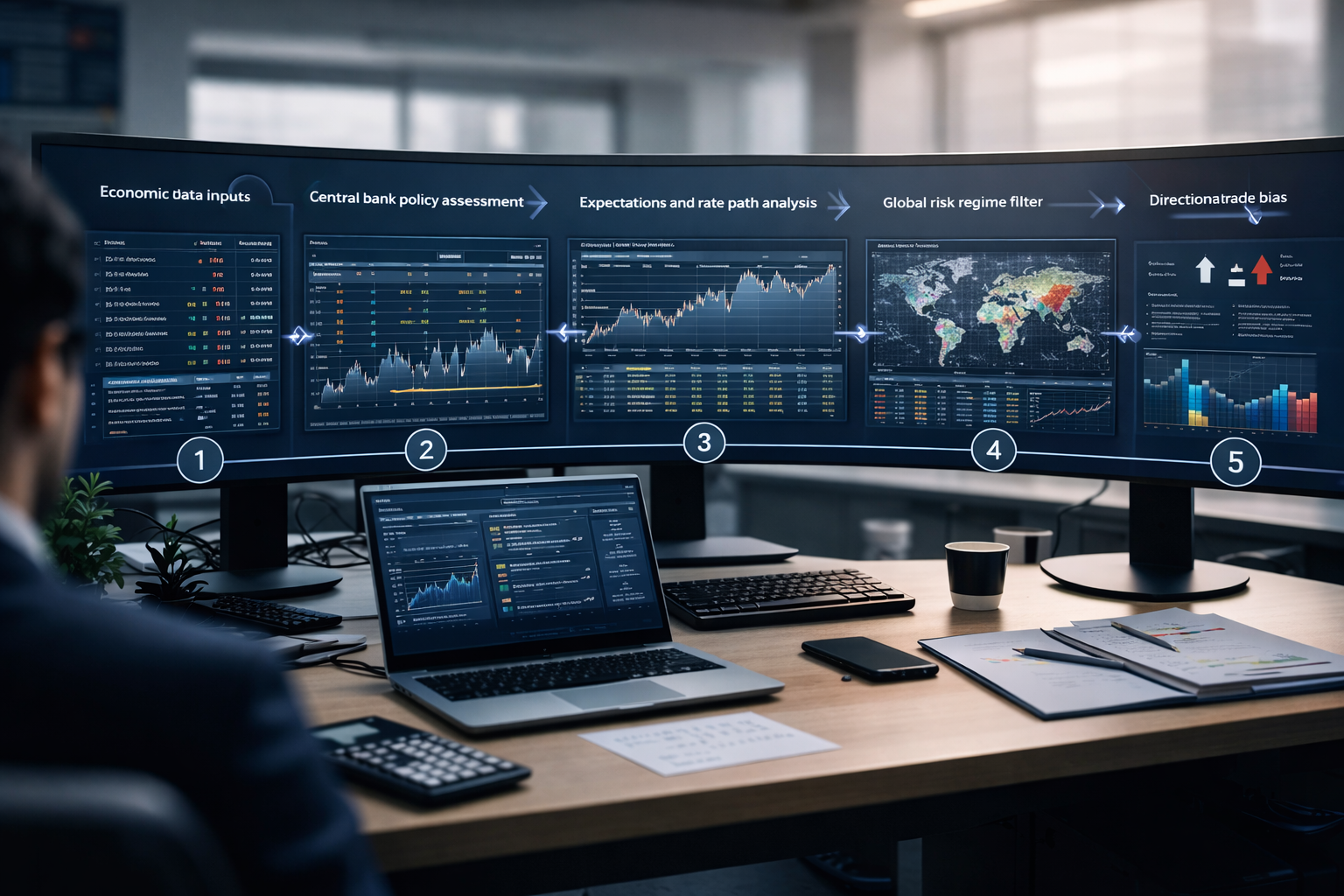

Step 1: Start with the currency pair and define the question
Fundamental analysis in forex is always relative. You are not asking whether a single currency is strong. Instead, you are asking whether one currency is fundamentally stronger than another over a specific time horizon.
Practical framing questions include:
- Is inflation more persistent in one economy than the other
- Is one central bank more hawkish or less dovish
- Is growth improving in one economy while weakening in the other
- Is one currency more exposed to global risk shifts
Step 2: Identify the macro drivers that matter for the current cycle
Not all data matters equally at all times. In a tightening cycle, inflation and labour data dominate. In a slowdown, growth and recession risks matter most. During crises, liquidity and risk overwhelm domestic fundamentals.
To prioritise correctly, ask:
- What is the market focused on right now
- What is the central bank’s reaction function
- Which data could realistically change rate expectations next
Step 3: Build the macro view using five core pillars
A professional forex fundamental analysis framework can be built around five pillars that apply across economies.
1) Inflation and monetary policy
Track headline and core inflation, services inflation, wage growth proxies, and the policy rate. Then assess whether inflation is falling fast enough for cuts or remaining sticky enough to justify restriction.
2) Economic growth
Monitor GDP, PMIs, industrial production, consumption data, and credit conditions. Focus on whether growth is surprising markets positively or negatively rather than on absolute levels.
3) Labour market conditions
Analyse unemployment, employment growth, participation rates, and wage pressure. Labour data often lags, so the key is identifying turning points rather than reacting to backward-looking strength.
4) External balances
Study trade balances, current account trends, energy sensitivity, and terms of trade. Economies with improving external positions are generally more resilient during periods of global stress.
5) Fiscal and business conditions
Evaluate budget balance trends, debt dynamics, business surveys, and confidence indicators. Fiscal credibility and policy stability increasingly influence currency risk premiums.
Step 4: Translate macro data into the central bank policy path
This step is where macroeconomic analysis becomes directly relevant to currency markets. Foreign exchange prices policy expectations more than raw data.
For each currency, define:
- The near-term policy bias
- The medium-term policy trajectory
- The dominant constraint, such as inflation stickiness or growth risk
Then compare those paths across the pair. When one central bank is expected to stay restrictive while the other is moving toward easing, relative currency strength often follows.
Step 5: Anchor analysis to expectations, not headlines
Currencies frequently move opposite to the news because markets trade the gap between expectations and reality.
Before reacting to data, ask:
- Was the result above or below consensus
- Did it alter the expected policy path
- Was the outcome already priced
- Did it change the broader narrative
If expectations remain unchanged, price reactions often fade.
Step 6: Apply the global regime filter
Even strong fundamentals can be overridden by global conditions. Therefore, always apply a regime filter before forming a trade bias.
A practical regime check includes:
- Equity volatility and trend
- Direction of real yields
- Credit market stress
- Demand for safe-haven assets
For example, in risk-off environments, high-beta currencies often weaken regardless of domestic data quality.
Step 7: Convert fundamentals into a clear trade bias
At this stage, reduce the analysis to a simple, testable statement:
- Which currency should outperform
- Over what time horizon
- What upcoming catalyst matters most
A professional bias always includes an invalidation point, defining what would prove the thesis wrong.
Step 8: Manage risk around events and narrative shifts
Fundamental analysis fails most often due to poor risk management. Therefore, always respect major data releases and central bank meetings.
Professional discipline includes:
- Reducing size ahead of binary events
- Avoiding overconfidence before policy decisions
- Reassessing the thesis after expectation shifts
- Writing invalidation rules before entry
A Worked Example Using Real Macro Logic
Consider a scenario where one economy has sticky services inflation and resilient employment, while another faces falling inflation, rising unemployment, and weakening business surveys.
In this case:
- The first central bank remains restrictive
- The second signals rate cuts
- Interest rate differentials widen
- Capital flows favour the higher expected real yield
As long as global risk conditions remain stable, the currency of the first economy tends to outperform the second. Crucially, the trade is driven by policy divergence, not by individual data releases.
Combining Fundamentals With Technical Analysis Properly
A professional workflow uses technicals as a risk and timing tool, not as a directional override.
The hierarchy is simple:
- Fundamentals define direction and horizon
- Sentiment shows whether the trade is crowded
- Technicals identify entry, exit, and invalidation
This structure prevents common errors such as abandoning a valid macro thesis due to short-term price noise.
Common Mistakes in Forex Fundamental Analysis
Trading headlines instead of expectations
Data only matters if it changes the policy path or narrative. If it was already priced, reactions are often temporary.
Ignoring relativity
Currencies trade against each other. A strong economy can still have a weak currency if the opposing economy is stronger or more hawkish.
Mixing time horizons
Macro analysis works best over weeks and months. Applying it to very short-term trading leads to overtrading and frustration.
Forgetting global regimes
Risk-off periods can overwhelm domestic fundamentals. Always assess the global backdrop.
Failing to define invalidation
Professional traders know what would prove them wrong. Without this, analysis turns into hope.
A Professional Weekly Routine for Forex Fundamental Analysis
Monday
Assess the global regime and identify the dominant macro themes.
Midweek
Update inflation, growth, labour, and policy expectations as data is released.
Thursday
Select currency pairs with the clearest divergence in policy paths.
Friday
Review expectation shifts and prepare for the following week’s catalysts.
FAQs
How does fundamental analysis work in forex
Fundamental analysis works by comparing economic conditions and policy expectations between two economies. Traders analyse inflation, growth, labour markets, and central bank signals to determine which currency should strengthen relative to another over a defined time horizon.
Why do currencies move based on fundamentals
Currencies move because fundamentals alter expectations for interest rates, real yields, growth, and capital flows. Since foreign exchange markets price the future rather than the present, even small changes in expectations can drive sustained currency moves.
Can beginners use forex fundamental analysis
Beginners can use a simplified framework focused on inflation trends, central bank stance, and growth momentum. By comparing these factors across two countries and tracking key economic releases, beginners can develop a structured and disciplined macro view.
What is macroeconomic analysis in forex
Macroeconomic analysis in forex examines how inflation, growth, labour markets, fiscal policy, and external balances influence central bank decisions and capital flows. In practice, it means translating macro data into a forward-looking policy path and relative currency bias.
How do you apply forex fundamentals to real trades
Apply fundamentals by defining direction and horizon first, then waiting for events that confirm or challenge the macro narrative. Use technical levels only for timing and risk control, trade changes in expectations rather than headlines, and reassess after major data or policy shifts.